Furnace Efficiency Guide: Maximizing Your Heating System’s Performance
Table of Contents
When it comes to heating your home, efficiency is critical for keeping your energy bills low and ensuring your furnace operates reliably throughout the cold months. A furnace that runs efficiently heats your home more quickly and evenly while using less fuel. In this Furnace Efficiency Guide, we’ll explore what furnace efficiency means, how to improve it, and why it’s essential for your comfort and budget.
Mountain Valley Plumbing in Loveland, CO, is prepared for emergencies with our availability. We offer prompt and reliable services to address urgent plumbing, heating, and cooling issues, ensuring that our clients’ needs are met swiftly and efficiently.
What is Furnace Efficiency?

Furnace efficiency refers to how well your heating system converts fuel into heat. It’s measured using the Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency (AFUE) rating, which indicates the percentage of fuel converted into usable heat for your home. For example, a furnace with an AFUE rating of 90% converts 90% of the fuel it uses into heat, with the remaining 10% lost as exhaust.
A higher AFUE rating means better efficiency, lower energy bills, and less environmental impact. Modern furnaces typically have AFUE ratings between 80% and 98.5%, with high-efficiency models delivering the most cost-effective and environmentally friendly heating.
Why Furnace Efficiency Matters
Improving furnace efficiency isn’t just about saving money—although that’s a big benefit. An efficient furnace reduces the fuel needed to heat your home, lowering your carbon footprint and helping reduce wear and tear on your heating system. The more efficiently your furnace runs, the less frequently it will need repairs and the longer its lifespan will be.
Moreover, with rising energy costs, maintaining a highly efficient furnace can significantly save your monthly utility bills. These savings can add up throughout a cold season, making efficiency a key factor in any homeowner’s heating strategy.
Types of Furnaces and Their Efficiency Levels
Several types of furnaces are on the market, each with varying efficiency levels. Here’s a breakdown of the most common types and their efficiency ratings:
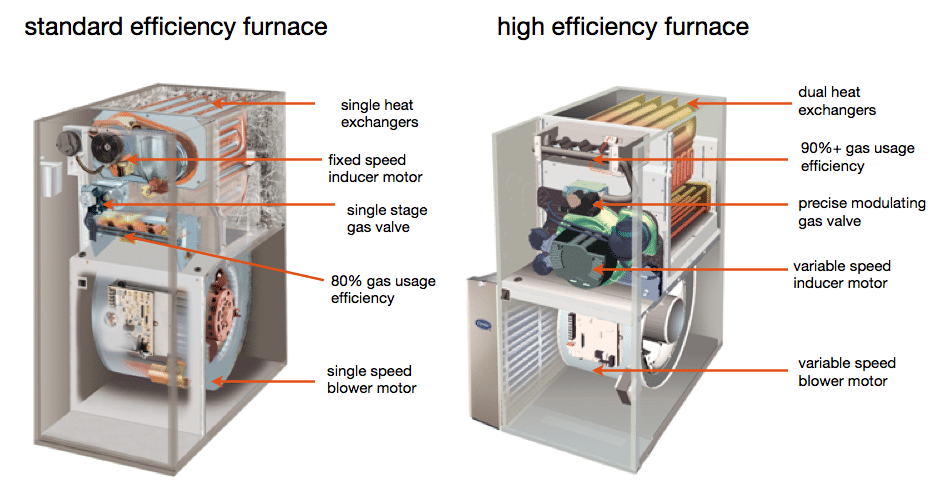
1. Standard Efficiency Furnaces
Standard efficiency furnaces typically have an AFUE rating between 80% and 85%. While less efficient than newer models, they can still provide reliable heating in mild climates. Although they lose a significant amount of heat through exhaust gases, they remain a common choice for homeowners due to their lower upfront cost.
2. High-Efficiency Furnaces
High-efficiency furnaces have AFUE ratings of 90% or higher, with some models reaching up to 98.5%. These systems use advanced technology, such as condensing heat exchangers and variable-speed blowers, to extract more heat from the fuel they burn. Although high-efficiency furnaces cost more upfront, they offer substantial savings on energy bills over time, making them a wise investment for homes in colder climates.
3. Two-Stage and Variable-Speed Furnaces
Two-stage furnaces operate at two levels of heating output: low and high. This allows them to run at a lower, more efficient setting most of the time, switching to the higher setting only when extra heat is needed. Variable-speed furnaces take this further by adjusting their blower speed to match your home’s heating needs more precisely. Both furnaces are designed to improve comfort and efficiency, providing consistent warmth without using excess energy.
Tips to Improve Furnace Efficiency

Even if you already have a high-efficiency furnace, there are several steps you can take to maximize its performance and reduce energy consumption. Here are some tips to help you get the most out of your heating system:
1. Regular Maintenance
Scheduling annual furnace tune-ups is one of the most effective ways to improve efficiency. A 22-point furnace tune-up checklist covers essential maintenance tasks such as cleaning components, tightening electrical connections, and calibrating the thermostat. These steps ensure your furnace operates at peak efficiency and can help prevent costly breakdowns.
2. Replace the Air Filter
A clogged air filter restricts airflow, causing your furnace to work harder and use more energy. Replacing your filter every 1-3 months ensures that air flows freely through the system, improving efficiency and indoor air quality.
3. Seal Air Leaks
Leaky ducts, windows, and doors can allow warm air to escape, forcing your furnace to work harder to maintain a comfortable temperature. Sealing these leaks with weather stripping, caulk, or duct tape can significantly improve your home’s energy efficiency.
4. Install a Programmable Thermostat
A programmable thermostat allows you to set your furnace to run only when needed, such as lowering the temperature when you’re away from home or asleep. This simple upgrade can lead to significant energy savings by reducing unnecessary heating.
5. Insulate Your Home
Proper insulation keeps warm air inside and cold air out, reducing the workload on your furnace. Attics, walls, and floors are common areas where additional insulation can help improve your home’s energy efficiency.
6. Upgrade to a High-Efficiency Furnace
If your furnace is over 15 years old, it may be time to consider upgrading to a high-efficiency model. While the initial cost of a new furnace can be high, the energy savings you’ll enjoy over the system’s life often offset the investment.
7. Use Ceiling Fans
In the winter, running your ceiling fans in reverse can help distribute warm air evenly throughout your home. This simple trick can reduce your furnace’s time to run, improving its efficiency.
Common Furnace Efficiency Problems
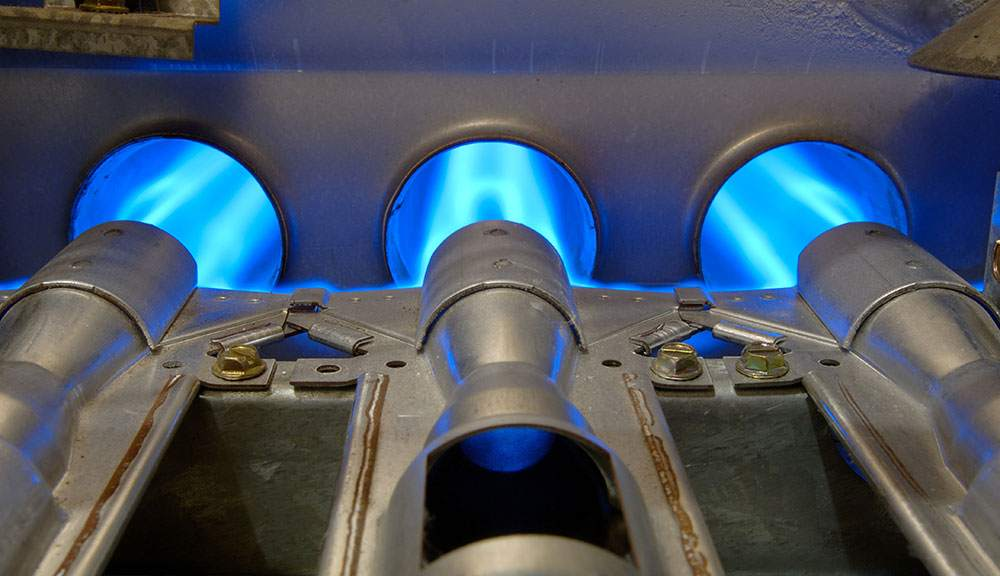

Several factors can negatively impact your furnace’s efficiency. Being aware of these issues can help you take preventive action and maintain optimal performance:
1. Dirty Burners
Burners clogged with dirt or debris can cause incomplete combustion, reducing your furnace’s efficiency. Regular cleaning of the burners is essential to ensure that your furnace operates at its best.
2. Cracked Heat Exchanger
A cracked heat exchanger reduces efficiency and poses a serious safety risk, as it can allow carbon monoxide to leak into your home. If your furnace is showing signs of a cracked heat exchanger, it’s crucial to have it inspected and repaired immediately.
3. Faulty Thermostat
A malfunctioning thermostat can cause your furnace to run longer than necessary or fail to maintain the desired temperature. If you notice your furnace cycling on and off frequently or not reaching the set temperature, the thermostat may be to blame.
4. Blocked Air Vents
Blocked or closed air vents prevent warm air from circulating properly throughout your home, forcing your furnace to work harder to heat your living space. Ensure that all vents are open and unobstructed to maximize airflow and efficiency.
How to Calculate Your Furnace’s Efficiency
To determine your furnace’s efficiency, start by finding its AFUE rating. This information is typically printed on the furnace’s data plate or available in the owner’s manual. Suppose your furnace doesn’t have an AFUE rating listed. In that case, you can calculate an approximate efficiency by comparing the fuel your system uses to the heat it produces.
Additionally, tracking your heating bills over time can provide insight into how efficiently your furnace operates. If you notice a sudden spike in your energy bills, it may be a sign that your furnace is no longer operating efficiently and needs maintenance or replacement.
Conclusion: Keep Your Furnace Efficient for Maximum Comfort and Savings
Furnace efficiency is critical in maintaining a comfortable home and checking your energy bills. By understanding the different types of furnaces and their efficiency levels and taking steps to improve and maintain your system, you can enjoy reliable heating while minimizing your environmental impact and energy costs.
FAQs
1. How often should I replace my furnace filter to improve efficiency?
You should replace your furnace filter every 1-3 months, depending on usage and the type of filter. A clean filter improves airflow and furnace efficiency.
2. Is upgrading to a high-efficiency furnace worth the investment?
Yes, upgrading to a high-efficiency furnace can significantly reduce energy bills, making it a worthwhile investment, especially for homes in colder climates.
3. Can a programmable thermostat save me money on heating?
Absolutely. A programmable thermostat helps reduce energy waste by allowing you to set specific temperatures for different times of the day, leading to significant savings on your heating bill.
4. What is the average lifespan of a high-efficiency furnace?
A high-efficiency furnace typically lasts 15 to 20 years. However, with regular maintenance and proper care, some units can last even longer.
5. How much can I save on energy bills with a high-efficiency furnace?
Upgrading to a high-efficiency furnace can reduce your energy bills by 20-30%, depending on your current system’s efficiency and how well your home is insulated.
6. How can I tell if my furnace is operating inefficiently?
Signs of an inefficient furnace include inconsistent heating, longer running times, higher energy bills, frequent cycling on and off, and strange noises during operation.
7. Can I improve my furnace’s efficiency without replacing it?
Yes, you can improve furnace efficiency through regular maintenance, such as cleaning or replacing filters, sealing air leaks, and ensuring the ductwork is clean and properly insulated.
8. Does furnace size affect efficiency?
Yes, the size of your furnace directly affects its efficiency. An oversized furnace cycles on and off more frequently, wasting energy, while an undersized furnace struggles to heat your home properly.
9. How often should I schedule a professional furnace tune-up?
It’s recommended to schedule a professional furnace tune-up once a year, ideally before the heating season begins, to ensure optimal efficiency and catch potential issues early.
10. What is the difference between a standard and a high-efficiency furnace?
A standard furnace typically has an AFUE rating of around 80%, meaning 20% of the energy is lost as exhaust. High-efficiency furnaces, on the other hand, have AFUE ratings of 90% or higher, meaning they convert more fuel into usable heat, making them more energy-efficient.
11. Can sealing my home’s windows and doors improve furnace efficiency?
Yes, sealing air leaks around windows, doors, and ducts can prevent heat loss. This allows your furnace to work less hard to maintain the desired indoor temperature, thus improving its efficiency.
12. How does insulation affect furnace efficiency?
Proper insulation in your home reduces heat loss, meaning your furnace doesn’t have to run as often or for as long, thereby improving its efficiency and reducing energy consumption.